3D Simulation Software Industry Transforming Design, Engineering, And Operations Worldwide Today
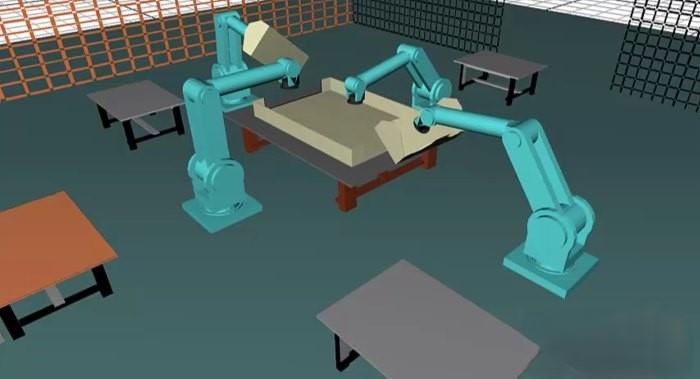
The 3D Simulation Software industry underpins digital engineering by enabling organizations to model, visualize, and test complex systems virtually before committing to physical prototypes. These tools span structural analysis, fluid dynamics, electromagnetics, multiphysics, kinematics, ergonomics, and virtual manufacturing, often integrated with 3D CAD and PLM environments. Automotive, aerospace, industrial equipment, electronics, energy, healthcare, and consumer‑products companies all rely on 3D simulation to optimize performance, weight, durability, safety, and cost. As products become smarter and more connected, simulation increasingly incorporates software behavior, controls, and human interactions, forming the foundation of digital‑twin strategies. High‑performance computing (HPC), cloud platforms, and GPU acceleration now make advanced simulations accessible to more engineers, shrinking development cycles and enabling broader design exploration.
Beyond traditional engineering, the 3D Simulation Software industry is expanding into operations and lifecycle management. Virtual commissioning of production lines, plant layout optimization, and logistics simulations reduce ramp‑up risks and improve throughput. In healthcare, patient‑specific anatomical models support surgical planning and medical‑device design. Built‑environment professionals use 3D simulation for energy modeling, airflow analysis, and occupant‑comfort assessments. Training organizations deploy immersive simulations for operator and safety training in hazardous industries, leveraging realistic physics and visual fidelity. These applications all share a common aim: de‑risking decisions by understanding complex interactions in a virtual environment where experimentation is cheaper, faster, and safer than in the real world.
Technology convergence is reshaping the sector. Real‑time physics engines, game‑engine rendering, and VR/AR interfaces bring simulation closer to interactive design reviews and human‑factors analysis. AI and machine learning assist with model reduction, design‑space exploration, and surrogate modeling, allowing rapid screening of thousands of variants. Parametric and generative‑design workflows couple 3D simulation with optimization algorithms to automatically propose novel geometries that meet multiple constraints. Meanwhile, APIs and open standards improve interoperability between CAD, PLM, MES, and IoT platforms, ensuring simulation data flows smoothly across the product lifecycle. Vendors increasingly offer cloud‑native solutions that combine scalability, collaboration, and pay‑as‑you‑go economics.
Looking ahead, the 3D Simulation Software industry will be integral to sustainability, resilience, and innovation agendas. Organizations face pressure to reduce emissions, material usage, and waste; simulation allows them to evaluate trade‑offs and design greener products and processes. Climate, supply‑chain, and cyber‑physical risks will be modeled more holistically, blending physics‑based and data‑driven approaches. Democratization is another theme: low‑code interfaces and templates will bring simulation to non‑specialist engineers, while centers of excellence oversee model governance and quality. Providers that combine deep physics, AI, cloud scalability, and strong ecosystem partnerships are positioned to lead as virtual experimentation becomes central to competitive advantage.
Top Trending Reports:
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Jogos
- Gardening
- Health
- Início
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Outro
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness
